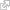The food chain of living things
Animals get their energy from food. Herbivores, like deer and hare, feed on plants. Carnivores, like lions and wolves, eat meat. Omnivores, which include pigs, bears, and humans, eat both plants and animals. In an ecosystem, all the organisms that depend on one another in order to eat form a food chain. Plants are at the bottom of this chain. They get their energy from the sun, which allows them to manufacture the substances they need for their development. Most animals depend directly or indirectly on plants. In this way, even carnivores that feed on herbivores depend on the plants that feed their prey.

- A superpredator is a carnivorous animal that is not the prey of any other species. It is at the top of the food chain. Raptors, tigers and wolves are examples of superpredators.
- The flesh of other animals is the principal food of carnivores. For example, snakes eat small rodents.
- Herbivores are animals that eat plants. Giraffes, which eat the leaves of acacia trees, are herbivores, as are certain rodents that eat seeds.
- Plants use the energy of the sun to manufacture the nutrients they need from the water, the carbon dioxide present in the air and the mineral elements in the soil. Trees, flowers, cereal grains, mosses and seaweeds are examples of plants.
- Decomposers feed on carcasses, excrement and plant remains. Bacteria, microscopic fungi and certain small animals, such as earthworms, are decomposers. In decomposing organic matter, they release mineral elements that are then used by plants to help them develop.
See also: Animal Kingdom, Vegetable Kingdom
Special relationships, for better or worse
Some organisms benefit from other species, without necessarily eating them. These special relationships have different names, depending on the type of association. Symbiosis is the association of two organisms of different species that mutually benefit from living together and cannot survive without each other. For example, coral is associated with algae, called zooxanthellae. It is a relationship that is vital to both. Mutualism is a relationship of mutual aid between two organisms of different species. In this way, the sea anemone and the clownfish protect each other, but their association is not vital. Commensalism is an association where one species benefits from another, without harming it or being beneficial to it. For example, the remora is a fish that attaches itself to another organism, such as a shark, and travels with it without disturbing it. Finally, parasitism is a harmful association, where one species lives off another, using that species’ resources for its own benefit. Certain flatworms, called tapeworms, parasitize the intestine of mammals.

Formed from the association of an alga and a fungus, lichens live in symbiosis. The alga manufactures the organic matter needed by both partners, while the fungus supplies them with water and mineral elements.

The dodder, a parasitic plant, has no leaves and is incapable of photosynthesis. Unlike other plants, it cannot use the sun’s energy in order to develop. It must live wound around the stalk of another plant, out of which it pumps organic matter using its suckers.

The remora, a fish of the tropical seas, attaches itself to the belly of a shark with an organ that acts like a suction cup. In this way, it travels long distances, benefiting from the protection of the shark and collecting its food scraps without harming it. This is called commensalism.
See also: Animal Kingdom, Vegetable Kingdom